Embryo transfer to a female uterus is one of the important steps of IVF Treatment, and the frozen embryo transfer procedure is one option for couples looking to start a family. When an egg is fertilized, it is known as Blastocyst or embryo.
During this procedure, a previously frozen blastocyst (a fertilized egg) is transferred to a female uterus with the hope of achieving a successful pregnancy. If you’re preparing for your first frozen blastocyst transfer, it’s normal to have a range of emotions and questions about what to expect. Understanding the procedure, the benefits and risks involved, and what you need to know before, during, and after the transfer can help ease your concerns and increase your chances of success.
In this blog, we will explore the world of frozen blastocysts and provide you with the information you need to feel confident and prepared for your journey toward parenthood.
You will hear from your IVF expert referring to the embryo as a blastocyst. Although, most people don’t have any understanding of the term.
So, what is a Blastocyst?
A blastocyst is a term used to describe a fertilized egg that has been developing for five to six days after fertilization. During in-vitro fertilization (IVF), The doctor will include using fertility medications for stimulating the ovaries into the release of healthy eggs. The eggs are then retrieved from the female ovaries and are sent to the lab for fertilization. After the fertilized eggs are multiplied, then it is transferred into the female uterus.
The blastocyst stage is an important milestone, as it is the point at which the fertilized egg has reached a stage of development where it can be successfully implanted into a woman’s uterus. The blastocyst contains an inner cell mass, which will eventually develop into the fetus, and an outer layer of cells that will form the placenta.
Lastly, the embryo should attach itself to the womb wall or female uterus for a pregnancy to begin.
When there is a need for embryo transfer?
IVF and embryo transfer are required in situations where natural fertilization is not a choice or has some problem from happening. Various other reasons are there for embryo transfer which includes:
- Few eggs are available for successful fertilization if the ovulation is infrequent. This is called ovulation disorder and in such cases, a doctor recommends IVF and embryo transfer.
- Fallopian tube damage is another problem when the doctor recommends IVF and blastocyst. Since the fallopian tubes are the road through which embryos travel to reaching the uterus. But when the tubes are damaged or blocked, it is improbable for fertilized eggs to reach the womb.
- Endometriosis is a chronic health condition in women of reproductive age, causing the tissue to grow outside your womb (uterus) on other reproductive organs. It can lead to affecting how the women’s reproduction functions, hence the only way out in such cases are IVF and blastocyst or embryo transfer.
- Premature ovarian failure occurs when ovaries are unable to produce the normal estrogen amounts or release the eggs naturally.
- Uterine fibroids are tiny tumors on the uterus wall which can cause the problem of inefficiency in an egg for planting itself in the uterus.
- Genetic disorders are also responsible for preventing pregnancy from happening and hence IVF and embryo transfer is initiated as a treatment.
- A low sperm count, impaired sperm, poor sperm motility, testes damage, semen anomalies are the causes of natural fertilization failure. Hence, IVF and blastocyst are the way out.
What is Frozen Blastocyst Transfer?
Frozen blastocyst transfer or frozen embryo transfer is a type of in-vitro fertilization (IVF) procedure in which a previously frozen blastocyst (a fertilized egg that has developed for five to six days) is transferred to a woman’s uterus.
This type of transfer is performed after the blastocyst has been frozen and stored for some time, allowing the couple to undergo additional rounds of IVF or to wait for a more favorable time for pregnancy. The process of freezing a blastocyst involves carefully preserving the fertilized egg in a controlled environment at extremely low temperatures.
When the couple is ready to proceed with a pregnancy, the frozen blastocyst is thawed and transferred to the uterus, where it can implant and develop into a fetus.
When to Consider Frozen Embryo Transfer (IVF-FET)?
Frozen blastocyst transfer offers several advantages, including increased chances of successful implantation, the ability to stagger treatments, and a reduced risk of multiple pregnancies. Here are a few reasons to consider frozen embryo transfer in IVF:
- When there is a need for more control over the timing of pregnancy
- When multiple rounds of IVF are planned
- When there are high-quality embryos available for freezing
- When there are medical conditions that may hamper the IVF process
- When there are financial considerations and the cost of multiple fresh IVF cycles is a concern
- When a previous fresh IVF cycle has not resulted in a successful pregnancy
Undergoing IVF treatment and a frozen embryo transfer can be overwhelming, especially if you’re unsure of how to prepare. To increase your chances of success, it is essential to start mentally and physically preparing as soon as you decide to pursue IVF and follow the essential tips for a successful IVF treatment.
It is also important to discuss all options with your IVF specialist to determine if frozen blastocyst transfer is the right choice for your personalized condition.
4 Stages of Implantation & Blastocyst
The process of implantation and the development of a blastocyst can be divided into four main stages. These stages include:
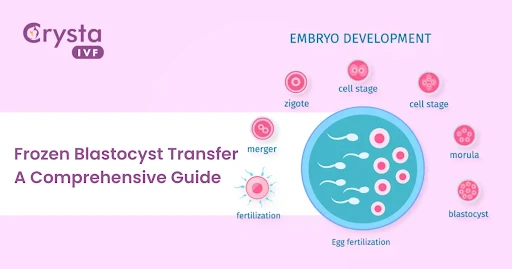
Fertilization: The first stage of implantation begins with the fertilization of an egg by sperm, resulting in the formation of a zygote.
Blastomere: Over the next few days, the zygote will divide into multiple cells, forming a blastomere.
Blastulation: After approximately five to six days of development, the blastomeres will form a fluid-filled structure called a blastocyst.
Implantation: The final blastocyst stage of the implantation process involves the blastocyst embedding into the endometrial lining of the uterus, where it will continue to develop into a fetus.
Read in Detail: 4 Stages of Implantation – Guide
What to expect during and after the embryo transfer?
The doctor will initiate the process by picking the finest eggs to transfer to the female womb around 2 or 3 days before the embryo transfer. Many processes are available there for aid selection, however, there are non-invasive methods like metabolic profiling that are in the process of testing. Metabolic profiling involves the selection of the finest eggs based on several varied factors. It can also lead to limiting the requirement for invasive procedures in the upcoming time. The fertilization of eggs takes place in the lab and is left to culture for around one or two days. If the quality of eggs is good and there are many, then the unused eggs can be frozen.
Embryo transfer process
The process of embryo transfer is similar to the process of a pap smear. The doctor will initiate the process by inserting a speculum into the female vagina so that the walls are open. Accuracy will be ensured through the use of ultrasound and then the doctor will begin the process by passing a catheter via the cervix and into the womb. Further, the embryos are passed through the tube and into the womb.
You don’t have to feel apprehensive about the pain as it is usually painless and very often needs sedatives. Some women may feel uneasiness as a consequence of the speculum insertion or from having a full bladder that is needed for the ultrasound.
After the embryo transfer
It will involve a follow-up appointment after two weeks to identify whether the transferred blastocyst was successful or not. Once the process is done, it is important to know that some women may experience some side effects such as bloating, vaginal discharge, and cramping.
Embryo transfers risks and precautions
Risks related to embryo transfers are not very high and are mostly associated with enhanced hormonal stimulation.
It leads to causing an augmented risk like blocking of a blood clot i.e. blood vessel. Some females may come across bleeding, variations in vaginal discharge, anesthesia complications, and infections.
The miscarriage risk is similar to the natural pregnancy.
However, the common IVF risks can be minimized when you closely work with your fertility doctor to address any complications beforehand.
Final thoughts
IVF and frozen blastocyst transfer can be effective solutions for couples who are struggling with infertility. With advances in technology and medical expertise, the success rates of IVF have greatly improved, making it an option that is worth exploring for those who want to start or grow their families.
The frozen blastocyst transfer procedure provides added control over the timing of pregnancy and can be a cost-effective alternative to multiple fresh IVF cycles.
It is important to work closely with an IVF specialist to understand all of your options and determine if this type of transfer is right for you.
You should get in touch with the right and best IVF Centre in Pune like Crysta IVF. We have been offering infertility services for years and have helped couples achieve pregnancy. You will find a team of the finest infertility experts having years of experience in the fertility industry.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey and there is hope for a successful outcome.
Updated on 01-04-25