Pregnancy in itself is a whole journey. Many people might think all the developments happen when the baby is an infant. However, that theory is a false one. All the crucial developments have already occurred before the baby is born, i.e., at the prenatal stage.
This prenatal development is also further divided into two stages:
- Embryonic stage– The first eight weeks of the pregnancy is the stage when the growth of the embryo takes place.
- Fetal stage– The fetal stage lasts from the ninth week of the pregnancy till the child’s birth.
The embryonic stage of pregnancy is the most critical stage. Many changes appear during this stage. In this blog, you will learn everything in detail about embryo development stages and what changes occur during this period.
First Stage- Fertilization
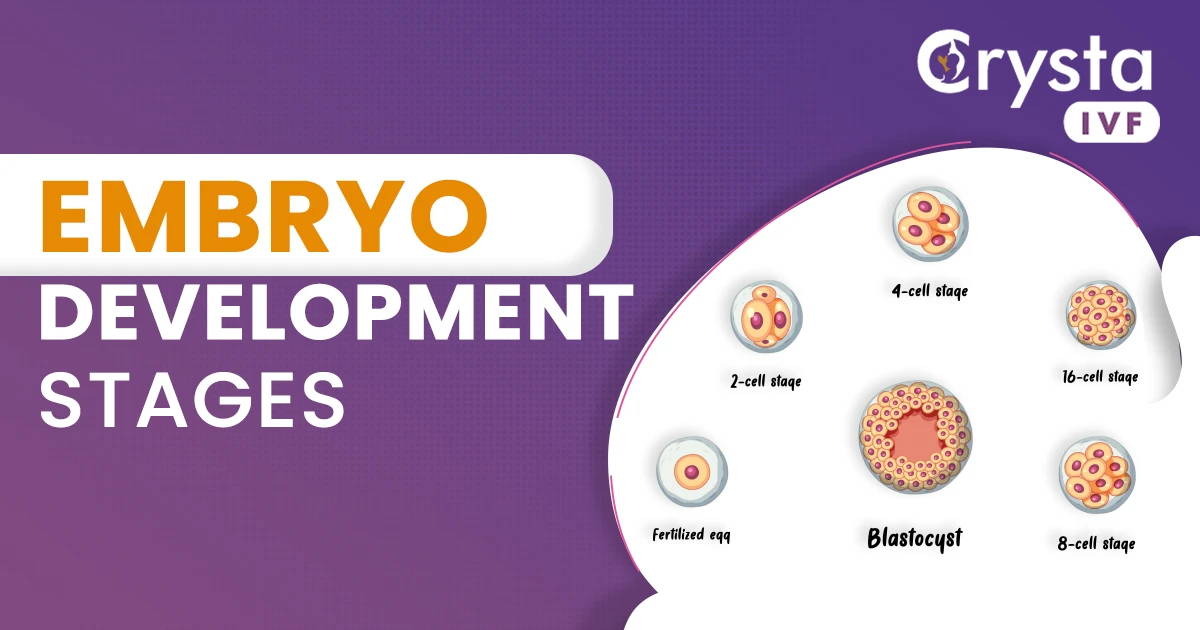
Fertilization is the simplest part of the whole process of embryonic development. During fertilization, the ovum (female gamete) and spermatozoa (male gamete) combine to form a zygote. Around 5 million sperms are released in the vagina during intercourse though most of the sperms die out before they reach the fallopian tube. Sperms can’t replicate, and the ones that last till ovulation unite with the egg to form the zygote. Fertilization not only occurs naturally but also can be processed artificially.
After fertilization, the zygote moves towards the uterus, and the zygote starts dividing and moving to the next stage to form blastocysts. All these things happen within 72 hours of the intercourse.
Also Read: Fresh or Frozen Embryo Transfer? A Never-Ending IVF Debate
Second Stage- Implantation
Blastocysts are small clusters of cells formed by the division that takes place in the fertilized egg (zygote). The formation of blastocysts starts around 5-7 days after fertilization. The cells in the blastocysts keep dividing till they form a protective layer called zona pellucida. The blastocysts stage is very important especially if the embryo is being formed through IVF (In-Vitro Fertilization).
The place near the uterus where the zona pellucida breaks and the blastocyst is released where the blastocyst implantation occurs. The blastocyst moves towards the uterus around the 10th day of the pregnancy. Implantation occurs in the outer lining of the uterus (endometrium), which forms the placenta in the future. The cells inside the zona pellucida mature and start forming cells for the heart, lungs, liver, tissues, bones, and skin form.
Also read: What are the positive signs to look after an embryo transfer?
Third Stage- Extra-Embryonic Membrane Formation
After implantation and the embryo’s embedding in the uterus, the embryo’s cells start to divide and form different membranes. Some cells move ahead and make the extraembryonic membrane, which supports and protects the fetus.
The extra-embryonic membranes that are formed are:
- Chronion
- The Yolk Sac
- Allaintios
- The Amnion
The amniotic cavity starts to form in the second week of pregnancy, and by the end, it is filled with amniotic fluid. This amniotic fluid protects the fetus from future trauma or injury. The kidneys aren’t formed until the 8th week of pregnancy, so the fetus’s urine is filled in the cavity along with the amniotic fluid. The embryo moves freely inside the cavity so that it can get used to the outside environment.
The Yolk Sac is formed along with the amnion on the opposite side of it. This yolk sac is used to nourish the embryo until the placenta is formed. After the placenta is formed, the yolk sac is reduced to being used just for blood circulation.
After the third week of pregnancy, a pocket-like structure starts forming at the end of the yolk sac. This structure is called Allaintos, and it functions as the fetus’s excretory organ.
On combining the yolk sac with allaintos, the umbilical cord is formed.
Also Read: Tips for Successful IVF Treatment & Frozen Embryo Transfer
Fourth Stage- Embryogenesis
The process of gastrulation, which causes the cells to change from totipotency to multipotency, causes the two-layered disc of cells to become a three-layered disc as the third week of development begins. The embryo, which assumes the appearance of an oval disc, creates a depression along the epiblast’s dorsal surface known as the primordial streak. Growth factors convey cells can proliferate and move. Two new cell layers are formed by the migration of cells toward, through, and then lateral to the original streak. The initial layer is the endoderm, a layer of cells that surrounds the yolk sac and pushes aside the hypoblast. The cells in the second layer are filled as the middle one.
The next stage of pregnancy begins when the ninth week starts after these processes. The stage from the ninth week is the fetal stage; this is when the embryo has finally turned into a fetus. The ninth week is the time around which the fetus is assigned its gender. Now, the growth and development of the organs and body of the fetus take place. The fetus even starts moving its body, but it only starts feeling prominent around the twentieth week.
The journey of embryo development is a miracle of nature, characterized by distinct stages crucial to life formation. From the fusion of gametes to the complex differentiation of tissues and organs, every step is arranged with so much precision. The process embodies the complexity of life’s beginnings, offering profound insights into our understanding of biology. Indeed, the journey from embryo to organism is a testament to the resilience and ingenuity of nature itself.
Read More Blogs:
The 4 Stages of Implantation: The Curtain Opens
Signs and Symptoms of Successful Implantation
Does Sperm Quality Affect IVF Success?
After How Many Weeks IVF Pregnancy Is Considered Safe